What’s the worst plague the human race has ever seen?
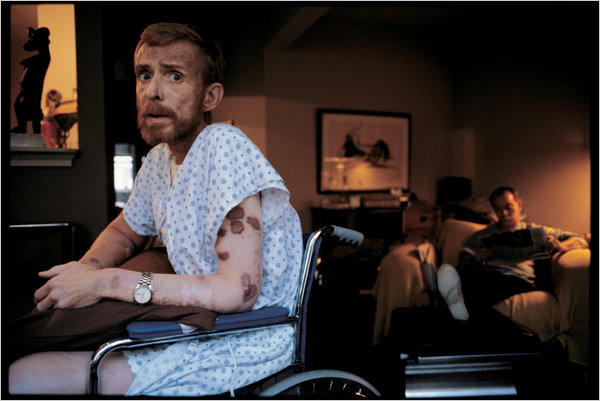
Black Death —bubonic plague – killed over 40 million people in 100 years. There was no medication.
AIDS killed 51.1 million people in 26 years (1997-2023).

Once medication became available, global HIV-related deaths reduced by 51%, claiming 69% fewer lives in 2023 since the peak in 2004, but still:
- an estimated 53,000–110,000 children died from HIV-related causes in 2023, and
- and estimated 430,000–730,000] adults died from HIV-related causes in 2023.
HIV/AIDS is the defining pandemic of our time.
- More than 38 million people are living with HIV, and only about 70% are on medication to prevent death from HIV advancing to AIDS.
- 16.5 million children worldwide have lost their mother, father or both parents due to HIV / AIDS as of 2016…
- around two-thirds of all young adults living with HIV are women, due to infected males having multiple female sexual partners.
If we include all sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), previously known as venereal diseases (VD), throughout human history, the numbers of dead are past counting. Clay tablets from Mesopotamia, Egyptian papyri, along with mythology, paintings of erotic scenes, and presence of prostitutes give sufficient information to indicate some forms of STDs were present among people at that time, and that these diseases were considered a divine punishment.
These validate the Biblical warning of consequences of promiscuity among the ancient Hebrews.
“If thou wilt diligently hearken to the voice of the Lord thy God, and wilt do that which is right in his sight, and wilt give ear to his commandments, and keep all his statutes, I will put none of these diseases upon thee, which I have brought upon the Egyptians.” (Exodus 15:26)
The writings of the Greek and Roman physicians and of their satiric poets (Martial, Juvenal, Ovid) described diverse genital diseases. Celsus described various diseases of the genitals. Galen coined the term gonorrhea – flow of semen.
The ancient Chinese and Indian physicians also gave some account on the presence of venereal diseases in their books, and the temple sculptures depict their sexual life.
The AIDS crisis, as we generally think of it, began in the 1980s. First as a mysterious illness primarily infecting gay men in urban areas in the United States. Over 30 new human pathogens have been detected in the last three decades, 75% of which have originated in animals like COVID’s suspected origination in bats, HIV originated in simians (monkeys and chimpanzees) in Africa.
But the AIDS virus didn’t make a random jump from animals to humans. It body slammed a particular population of people.
Like COVID. More than 81% of COVID-19 deaths occur in people over age 65 The number of deaths among people over age 65 is 97 times higher than the number of deaths among people ages 18-29 years.
A person’s risk of severe illness from COVID-19 increases as the number of underlying medical conditions they have increases.
Likewise, AIDS – the full blown disease – began, and HIV – the latent infection – remains, very much in the majority in a certain population because of the number of underlying medical conditions common within that population.
Men who have sex with men (MSM) have been the population most impacted by the epidemic since the beginning. If current rates continue, it is estimated that 1 in 6 MSM will be diagnosed with HIV at some point in their lives.
- MSM make up an estimated 2% of the US population, but accounted for 66% of new annual HIV infections in 2017.
- As of 2018, 1 in 6 MSM living with HIV was unaware of their status – and pass it on to unwitting partners.
- As of 2019, 56% of people living with HIV in the US contracted it through male-to-male sexual transmission.
The reason for this is vulnerability to infection due to reduced immune responses from the number of underlying infections already experienced.
From the National Library of Medicine, 2014
It was not an accident that the AIDS epidemic first struck MSM [males having sex with males, the politically correct term replacing homosexual to demonstrate destigmatization]. Even before the first MSM was infected with the virus, MSM were already in the midst of an epidemic of STDs. MSM were at risk for
- syphilis,
- gonorrhea,
- hepatitis A,
- hepatitis B,
- hepatitis C,
- cytomegalovirus,
- Epstein-Barr virus,
- human papillomavirus,
- chancroid,
- lymphogranuloma venereum,
- granuloma inguinale,
- pubic lice,
- pinworms,
- scabies,
- flea bites.
A survey of 4212 MSM found that “the number of different lifetime sexual partners best predicted the number of venereal infections”. During the pre-AIDS period, infection with a STD carried no stigma within the gay community. The ritual of repeated infection and treatment had become part of the gay lifestyle.
“Promiscuity … was central to the raucous gay movement of the 1970s.” In the fall of 1980, Dr. Selma Dritz, the infectious disease specialist for the San Francisco Department of Public Health, warned:
Too much is being transmitted …if something new gets loose here, we’re going to have hell to pay
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is not easily transmitted. It requires percutaneous or mucosal contact with blood or other body fluids…
In 1981 and 1982 CDC researchers conducted in-depth interviews with the first AIDS patients. They were shocked by the sheer number of sexual partners reported, typically over 1000.The virus spread quickly. For example, in 1983, the HIV seroprevalence among MSM tested in a Baltimore STD clinic was 14 percent. One year later, it was 58 percent…
HIV infection usually doesn’t kill outright, but destroys the immune system, making its victims…vulnerable to a host of diseases, including
- toxoplasmosis (a cat disease),
- cryptococcal meningitis,
- candidiasis,
- severe herpes,
- Cryptosporidium (an animal parasite),
- encephalitis,
- a fulminant form of Kaposi’s sarcoma (a skin cancer previously found mainly in older men of Mediterranean origin).
#1: HIV/AIDS – Although HIV is now a disease that can be managed, there is still no cure, and preventing infection remains the key to ending the epidemic.
#2: Anal Papilloma – cause certain types of anal cancers.
#3: Hepatitis – can cause serious health problems, including liver cancer, cirrhosis, liver failure, and even death. Safe sex, which reduces the risk of transmission of all types of viral hepatitis, is the only way to prevent transmitting hepatitis C.
#4: Substance Use – Gay men abuse substances at higher rates compared to others.Use of these drugs has been linked to higher rates of HIV transmission through impaired decision making during sex. Although the long-term effects are unknown, evidence suggests that prolonged use of these substances is likely to have serious negative health consequences.
#5: Depression and Anxiety – Men who have sex with men have higher rates of depression and anxiety compared to others. These problems are often worse for men who are closeted or don’t have adequate social support. Not mentioned in this article but obviously a cause for depression is the constant abandonment experienced in the promiscuous lifestyle.
#6: Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) These include infections for which there are effective cures (gonorrhea, chlamydia, syphilis, pubic lice or crabs), as well as those for which treatments are more limited (HIV, hepatitis A, B, or C, human papilloma virus). Safe sex, including the use of condoms, is key to preventing STDs.
#7: Prostate, Testicular, and Colon Cancer
#8: Alcohol -Studies show that men who have sex with men have higher rates of alcohol abuse and dependence…and can increase the risk for being injured or becoming the victim of a crime.
#9: Tobacco – Gay men smoke and use tobacco products at much higher rates than others. This can lead to a number of serious health problems, including heart disease, high blood pressure, lung disease, and lung cancer.
#10: Body image problems and obesity – Men who have sex with men are more likely to have body image problems than others. This includes higher rates of eating disorders, such as anorexia nervosa and bulimia. Also, using anabolic steroids and nutritional supplements can be unhealthy. Obesity is also a problem among some gay men, and this can lead to heart disease and diabetes.
So why pursue the high-risk gay lifestyle?
Actual scientific research into the LGBT+ lifestyle has established factual evidence that experiences drive sexual preferences and behaviors drive compulsions. Massive Study Finds No Single Genetic Cause of Same-Sex Sexual Behavior, By Sara Reardon on
Compulsive sexual behavior is sometimes called hypersexuality, hypersexuality disorder or sexual addiction. It’s an excessive preoccupation with sexual fantasies, urges or behaviors that is difficult to control, causes you distress, or negatively affects your health, job, relationships or other parts of your life.
Some indications that you may be struggling with compulsive sexual behavior include:
- You have recurrent and intense sexual fantasies, urges and behaviors that take up a lot of your time and feel as if they’re beyond your control.
- You feel driven to do certain sexual behaviors, feel a release of the tension afterward, but also feel guilt or remorse.
- You’ve tried unsuccessfully to reduce or control your sexual fantasies, urges or behavior.
- You use compulsive sexual behavior as an escape from other problems, such as loneliness, depression, anxiety or stress.
- You continue to engage in sexual behaviors that have serious consequences, such as the potential for getting or giving someone else a sexually transmitted infection, the loss of important relationships, trouble at work, financial strain, or legal problems.
- You have trouble establishing and maintaining healthy and stable relationships.